Zero Knowledge Proofs Explained: A Complete and Practical Guide
Learn how zero knowledge proof technology works, where it is used in blockchain and crypto, and how the Zero Knowledge Proof (ZKP) crypto project applies it in practice.
Release Date: February 2, 2026

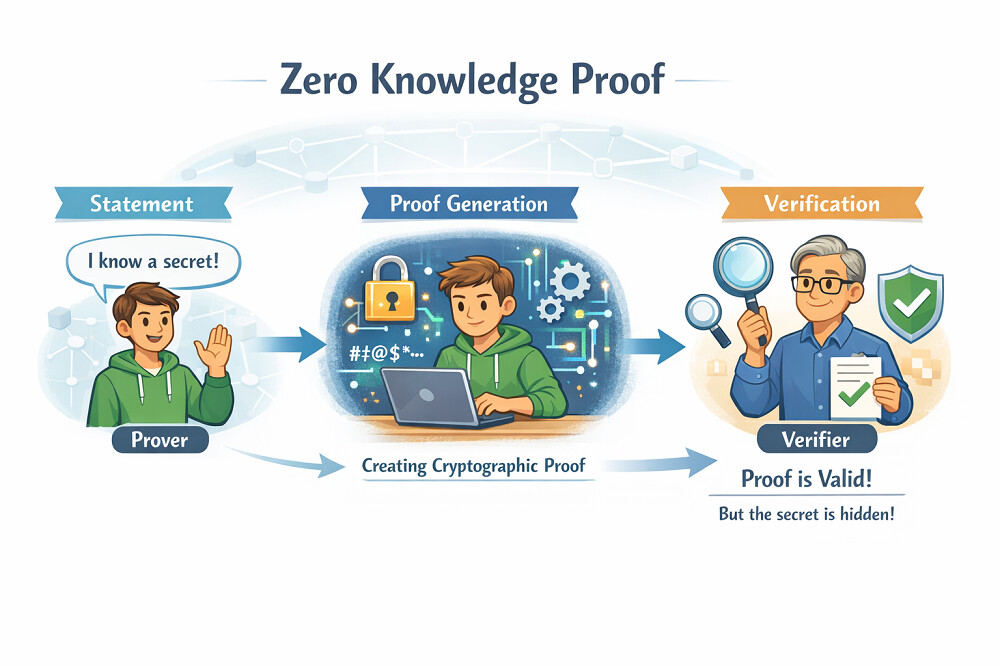
Zero knowledge proof sounds like a paradox, but it is one of the most powerful ideas in modern cryptography. Zero knowledge proof is a cryptographic method that allows one party to prove that a statement is true without revealing the underlying data that makes the statement true. Rather than sharing sensitive information, the prover generates a cryptographic proof that can be independently verified by others, confirming correctness without disclosure.
Zero knowledge proof technology is becoming essential as digital systems seek to balance transparency, privacy, and trust. Traditional verification methods rely on exposure, requiring users to reveal sensitive data, which creates security and privacy risks. Zero knowledge proofs offer a trustless alternative, allowing systems to verify correctness without accessing private information. This is especially important in blockchain, where transparency enables auditability but exposes user activity. Zero knowledge proof based blockchains solve this by verifying transactions and rules without revealing sensitive on-chain data.
This article explains how zero knowledge proof technology works, where it is used in blockchain and crypto, and how the Zero Knowledge Proof (ZKP) crypto project applies it in practice.
What Is Zero Knowledge Proof Technology?
Zero knowledge proof technology is based on a simple idea: one party can prove that a statement is true without revealing the information that makes it true.
There are two roles involved:
Prover: the party that knows a secret or valid solution
Verifier: the party that needs confirmation
The prover wants to show that a claim is correct. This might mean proving they know a password, that a transaction follows network rules, or that they meet certain requirements. Instead of revealing the secret itself, the prover generates a cryptographic proof that confirms the claim is valid.
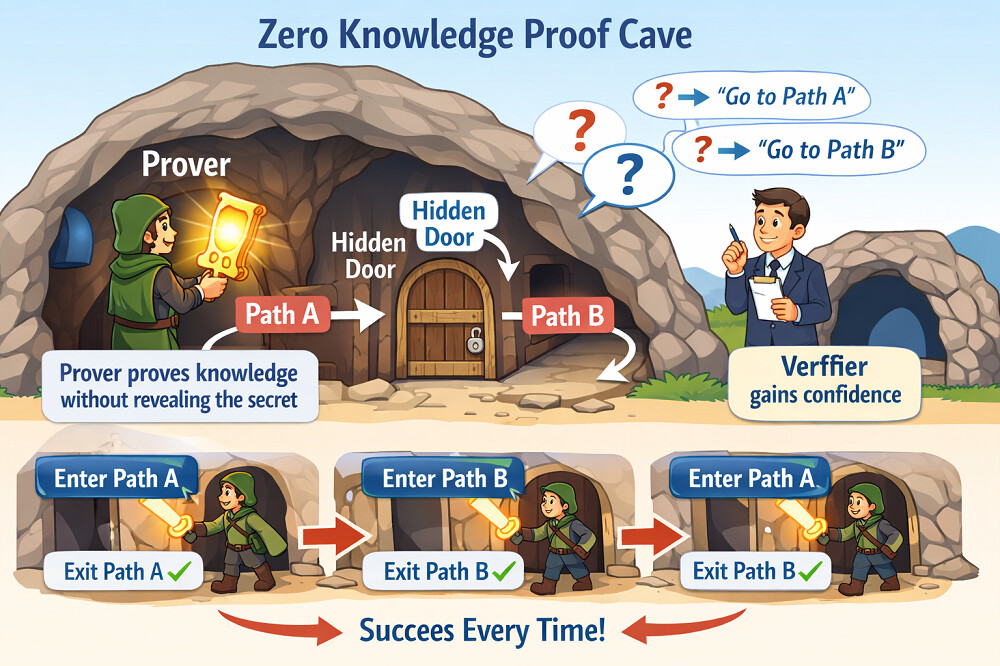
Imagine a cave with two paths connected by a hidden door. The prover says they know the secret phrase that opens the door. The verifier stays outside and asks the prover to come back through one of the two paths, chosen at random. If the prover truly knows the secret, they can always return through the requested path. After seeing this happen repeatedly, the verifier becomes confident that the prover knows the secret, even though the phrase is never revealed.
This example shows the core idea behind zero knowledge proof technology: the verifier gains confidence without learning the secret itself.
Key Cryptographic Properties
Every zero knowledge proof must satisfy three cryptographic properties.
Completeness
If the statement is true and the prover follows the protocol correctly, the verifier will accept the proof.Soundness
If the statement is false, it is computationally infeasible for a dishonest prover to convince the verifier. Any chance of cheating is limited to a negligible probability.Zero-knowledge
The verifier learns nothing beyond the fact that the statement is true. No additional information is leaked.
It is important to note that zero knowledge proofs rely on probabilistic security. They do not offer absolute guarantees, but the probability of deception can be reduced to such a low level that it is considered cryptographically secure.
How Do Zero Knowledge Proofs Actually Work?
Zero knowledge proofs rely on structured verification processes rather than information sharing. These processes can be interactive or non-interactive, with non-interactive proofs forming the basis of most blockchain systems today.
Interactive vs Non-Interactive Proofs
Modern zero knowledge proof blockchain systems rely on non-interactive proofs. In this model:
The prover generates a single proof
The proof can be shared publicly
Anyone can verify it independently
Protocols such as zk-SNARKs and zk-STARKs are non-interactive and form the foundation of most zero knowledge proof crypto systems today.
How to Make a Zero-Knowledge Proof?
Every zero knowledge proof system includes four conceptual components:
Prover: holds private data or a secret witness
Verifier: checks the proof
Statement: the claim being proven true
Proof: cryptographic evidence of correctness
From a developer's perspective, the prover encodes rules into a circuit or program that defines what “valid” means. The proof demonstrates that the prover executed this logic correctly using valid inputs, without revealing those inputs. The verifier checks the proof using public parameters and cryptographic rules.
Use Case: What is a Practical Example of ZKP?
The following examples illustrate how zero knowledge proof technology enables verification across blockchain systems and identity use cases without revealing sensitive data.
A Simple Zero Knowledge Proof Analogy
One of the easiest ways to understand zero knowledge proof technology is through a simple real-world scenario. A commonly used example is a cave with two paths connected by a hidden door. The prover claims to know a secret phrase that opens the door. The verifier waits outside and randomly asks the prover to return through one of the two paths. If the prover truly knows the secret, they can always comply. After repeated success, the verifier becomes confident that the prover knows the secret, even though the phrase itself is never revealed.
This shows how verification can occur without disclosure.
What is a ZK in Crypto? A New Model for Blockchain Privacy
The same logic applies in blockchain environments. In traditional systems like Bitcoin, transactions are fully transparent. Sender addresses, receiver addresses, and transaction amounts are visible to anyone. While this supports auditability, it also exposes user behavior and financial data.
Zero knowledge proof blockchain systems introduce a different approach. Instead of revealing all transaction data, the network uses cryptographic proofs to verify that rules are followed. Transactions can be confirmed as valid without exposing sensitive details. The network can still ensure that balances are correct, protocol constraints are respected, and double-spending does not occur.
This model allows blockchains to preserve trustless verification while reducing unnecessary data exposure. As blockchains expand into payments, identity, and enterprise use cases, zero knowledge proofs help balance transparency with privacy.
Selective Disclosure and Identity Verification
Zero knowledge proof technology also enables selective disclosure beyond transactions. A user can prove they meet a requirement, such as being over a certain age or eligible to participate, without revealing personal identity information or documents. This capability is increasingly important for decentralized identity systems, compliance-aware applications, and privacy-preserving access control.
Together, these examples illustrate how zero knowledge proof crypto systems provide verifiable correctness while protecting user privacy.
How to Make a Zero-Knowledge Proof?
This section explains the basic steps behind creating a zero knowledge proof and introduces the main proof systems used in blockchain environments.
The Conceptual Process
Creating a zero knowledge proof follows a structured process designed to verify correctness without revealing private data.
First, a clear statement is defined. This is the claim that needs to be proven true.
Next, the rules that determine validity are encoded into a cryptographic system.
The prover then generates a proof using private inputs that satisfy those rules.
Finally, the verifier checks the proof using public information to confirm correctness.
Throughout this process, the underlying data remains private. Only the validity of the statement is revealed, not the information used to prove it.
ZK-SNARKs and ZK-STARKs
Two major families of zero knowledge proof technology are commonly used in blockchain systems.
zk-SNARKs are designed to produce compact proofs that are fast to verify, which makes them well-suited for on-chain validation. However, many implementations rely on a trusted setup phase.
zk-STARKs remove the need for trusted setups and focus on transparency and scalability. The tradeoff is that proofs are typically larger and require more computational resources.
Both approaches support non-interactive verification and are widely used across zero knowledge proof blockchain systems today.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchains Using Zero Knowledge Proofs
Zero knowledge proof technology has become a foundational tool in modern blockchain systems. By allowing verification without disclosure, ZK proofs enable privacy, scalability, and trustless verification while maintaining network integrity and security. Below are some of the main areas where zero knowledge proofs are applied in blockchain.
Privacy Coins
Privacy-focused cryptocurrencies were among the first blockchain applications of zero knowledge proofs. They allow verification of transactions without exposing sensitive details.
Zcash (ZEC)
Zcash (ZEC) uses zk-SNARKs to validate transactions without revealing sender and receiver addresses or transaction amounts. This allows the network to confirm that coins are legitimate and not double-spent while keeping financial details confidential.
Zero Knowledge Proof (ZKP)
The ZKP crypto project applies zero knowledge proof technology to support privacy-preserving AI infrastructure. The network enables verifiable computations and interactions without exposing sensitive data, ensuring that both transactions and AI-driven processes remain confidential. By combining zero knowledge proofs with AI task validation, the system demonstrates how privacy can be integrated into complex, data-driven environments.
Other privacy-oriented cryptocurrencies adopt similar principles, emphasizing selective disclosure, confidentiality, and cryptographic verification to protect users’ information while maintaining blockchain correctness.
Layer-2 Scalability Solutions
Zero knowledge proofs are increasingly used to improve the scalability of blockchains. Layer-2 solutions like StarkNet, zkSync, and Loopring leverage ZK proofs to bundle large batches of transactions off-chain. Instead of processing every transaction individually on the main chain, these systems generate a single cryptographic proof that confirms all bundled transactions are valid.
This approach significantly reduces network congestion and transaction costs, as fewer on-chain operations are required. At the same time, security and correctness are preserved because the proof is publicly verifiable, allowing anyone to check that the transactions comply with protocol rules.
By combining privacy and efficiency, these systems show how zero knowledge proofs can enhance blockchain usability at scale.
Broader Blockchain Use Cases
Beyond financial transactions and scalability, zero knowledge proof technology is increasingly applied to a wide range of blockchain applications:
Decentralized Identity Verification: Users can prove attributes about themselves, such as age or membership, without revealing personal information. This enables privacy-preserving access control and authentication.
Verifiable Credentials: Individuals or organizations can validate qualifications, certifications, or other credentials using zero knowledge proofs, ensuring trust without exposing sensitive details.
Privacy-Preserving Computation: Smart contracts or decentralized applications can perform computations on private inputs, proving correct outcomes without exposing the underlying data.
Supply Chain Verification: Companies can validate product provenance or compliance with standards without revealing proprietary information.
These applications demonstrate that zero knowledge proofs are not limited to payments. They provide a framework for privacy, trustless verification, and efficiency across many blockchain-based systems, making them a versatile tool for the next generation of decentralized technologies.
Why Zero Knowledge Proofs Matter for Blockchain and Beyond?
Zero knowledge proof technology is transforming the way digital systems handle verification, security, and privacy. By allowing correctness to be proven without revealing sensitive data, ZK proofs address critical challenges in blockchain and beyond.
Privacy Preservation
Zero knowledge proofs enable systems to confirm the validity of transactions or computations without exposing underlying data. This protects personal, financial, or operational information while still allowing trustless verification. Privacy preservation is particularly important as blockchains expand into identity, governance, and enterprise use cases.Security and Integrity
ZK proofs ensure that rules are enforced and operations are valid without relying on intermediaries. Networks can prevent fraud, double-spending, and rule violations while maintaining a decentralized, trustless model. This strengthens overall system security and reduces dependence on central authorities.Scalability and Performance
Non-interactive proofs, like zk-SNARKs and zk-STARKs, condense multiple computations or transactions into a single cryptographic proof. This reduces on-chain processing, minimizes storage requirements, and allows networks to handle higher throughput efficiently without compromising correctness.Regulatory Compliance
Zero knowledge proofs provide a way to demonstrate adherence to rules or policies without exposing private data. This makes it easier to comply with privacy regulations such as GDPR, enabling organizations to verify eligibility, consent, or transaction validity while minimizing legal risk.
By combining privacy, security, scalability, and regulatory alignment, zero knowledge proofs form a foundational technology for next-generation blockchain networks and other systems that require verifiable, confidential, and efficient operations.
Challenges and Misconceptions Around ZK Technology
While zero knowledge proof technology offers significant advantages for privacy, security, and scalability, it also faces several challenges and common misunderstandings. Understanding these limitations is important for evaluating the technology and its practical applications.
Complexity Barrier: Designing ZK systems requires advanced cryptography and careful programming. Creating proofs involves encoding rules into circuits or programs, which can be intricate and slow down development or auditing.
Misunderstanding “Zero Knowledge”: The term often confuses people. It does not mean no data or computation is involved; it means only the truth of a statement is revealed, without exposing the underlying information. Misinterpretation can lead to overestimating privacy guarantees or applying the technology incorrectly.
Performance and Computational Cost: Generating some zero knowledge proofs can demand significant computation and memory, potentially affecting transaction speed and network efficiency. Non-interactive proofs like zk-SNARKs and zk-STARKs improve performance, but trade-offs remain between proof size, verification time, and cryptographic security.
Despite these hurdles, ongoing research and protocol improvements are steadily reducing complexity and computational overhead, making zero knowledge proofs increasingly feasible for real-world blockchain applications and other privacy-sensitive systems.
Zero Knowledge Proof (ZKP) Blockchain Network
The Zero Knowledge Proof (ZKP) is a blockchain network built around zero knowledge proof technology, designed to enable private and verifiable computation in distributed systems. Instead of relying on traditional data disclosure, the network uses cryptographic verification to support secure processing and collaboration around sensitive information.
Vision and Mission
The ZKP project aims to shift control of computation and data back to the users who generate and own it. Its mission is to decentralize high-performance workloads and artificial intelligence (AI) systems, making them verifiable and private while avoiding reliance on centralized infrastructure. In this model, privacy and correctness are enforced through cryptographic proofs rather than trust in an intermediary.
The project emphasizes a modular and flexible architecture with a hybrid consensus model that rewards useful computation and storage contributions across a distributed network.
Technology and Innovation
The ZKP project integrates zero knowledge proof principles into key blockchain operations:
Token Distribution: ZKP uses a daily on-chain presale auction. Participants contribute crypto assets to receive a share of the day’s tokens. Cryptographic proofs ensure each participant receives their fair share according to the rules, without revealing private data.
Auction Fairness: To ensure fairness in the presale auction and token distribution, all contributions are verified and recorded publicly. Allocations are proportional to each participant’s share of the pool. This eliminates private rounds or preferential pricing.
On-Chain Verifiability: Every computation, token allocation, and transaction is validated using cryptographic proofs, allowing independent verification without exposing underlying data.
How the ZKP Project Applies Zero Knowledge Proof in Practice?
This section highlights the practical ways ZKP leverages cryptographic proofs to validate operations, maintain transparency, and support equitable participation.
Verifiable Rules and Open Participation
The ZKP presale auction runs on a proportional, on-chain system that resets every 24 hours, so participants can join at any time without worrying much about price swings. Contributions are verified in real time and recorded on-chain, ensuring transparency and fairness.
Zero knowledge proofs guarantee that all allocations follow the rules without exposing private data, giving everyone equal access and confidence in the process.
Benefits to Participants
Trustless Verification: Users can independently check that operations and allocations adhere to the rules.
Equal Access: Participation is open and proportional, ensuring that no individual or group receives undue advantage.
Secure, Proof-Based Enforcement: All network processes are backed by mathematical proofs, reducing the risk of errors or manipulation.
By combining transparent verification, equal participation, and cryptographically enforced rules, the ZKP network demonstrates a real-world application of zero knowledge proof technology. It shows how fairness, security, and privacy can coexist in a decentralized ecosystem.
Future of Zero Knowledge Proof and Crypto
Zero knowledge proof technology is set to play a major role in blockchain and digital systems as privacy and secure verification become essential. The global ZKP market is projected to grow rapidly, driven by demand in finance, healthcare, identity, and decentralized applications.
Emerging use cases go beyond traditional blockchain payments. Research highlights potential in decentralized identity and verifiable credentials, where users can prove assertions without revealing underlying data. [1]
Zero knowledge proofs are also being studied for IoT authentication, enabling devices to validate actions without sharing private inputs, and for secure voting systems that confirm vote integrity without exposing individual choices. [2]
At the protocol level, ongoing development of zk‑SNARKs and zk‑STARKs continues to improve efficiency, proof size, and verification speed. These advancements, combined with growing tooling and developer resources, make ZK proofs more practical for large-scale deployment across multiple sectors.
Overall, trends suggest a future where zero knowledge proofs enable privacy-preserving, verifiable digital ecosystems in both blockchain and broader applications.
Final Thoughts
Zero knowledge proofs provide a powerful way to verify truth without revealing sensitive data, offering privacy, security, and trustless verification across digital systems. They are critical for building transparent and secure blockchain applications while protecting user information.
The ZKP network applies these principles in practice, ensuring equitable participation, transparent token allocation, and verifiable operations through on-chain cryptographic rules. By doing so, it demonstrates how zero knowledge proofs can create privacy-preserving yet auditable systems that everyone can trust.
Learn more about the Zero Knowledge Proof (ZKP) and see how these principles are applied to create a transparent, privacy-focused ecosystem.
FAQs
Q1: What is a zero knowledge proof?
A: A zero knowledge proof is a cryptographic method that allows one party to prove a statement is true without revealing the underlying data. It ensures trust, privacy, and verification simultaneously.
Q2: How do zero knowledge proofs work?
A: The prover generates a cryptographic proof of correctness based on private inputs. The verifier checks the proof without accessing the original data. Non-interactive proofs, such as zk-SNARKs and zk-STARKs, are commonly used in blockchain systems.
Q3: What are the main types of zero knowledge proofs?
zk-SNARKs: Compact, fast to verify, and usually require a trusted setup.
zk-STARKs: Transparent, scalable, larger proof sizes, no trusted setup required.
Q4: Which cryptocurrencies use zero knowledge proofs?
A: Privacy coins like ZKP crypto and Zcash uses zero knowledge proofs. Layer-2 scalability solutions such as StarkNet, zkSync, and Loopring also rely on ZK proofs to compress and validate transactions efficiently.
Q5: What is Zero Knowledge Proof (ZKP)?
A: Zero Knowledge Proof (ZKP) is a privacy-first decentralized ecosystem for artificial intelligence (AI). It enables secure computation, data exchange, and collaboration between users, developers, and institutions without exposing private data.
Keep Reading Blog Posts
You've just scratched the surface — dive deeper into the fundamentals of ZKP.